Best Practices for Security for Flutter Application
Research Piece
Flutter is a mobile app development system that supports the cross-deployment of apps in programming.
Code obfuscation
- Flutter apps should be equipped to prevent hackers from reverse engineering the app code and leaking strings, methods, API keys and class names. Data should not be stored in plain text. Techniques such as obfuscation can hide functions and class names compiled in Dart code.
API key security
- Restrictions should be applied to limit applications, websites and IP addresses that can access API keys. Encryption and decryption methods should be applied to API keys on runtime. API keys should not be tracked on the repository to minimise the exposure of values.
Flutter jailbreak detection
- To prevent security threats and safeguard applications from a jailbroken device, the package ‘Flutter_jailbreak_detection’ can be used. This will determine if the app is being run on a compromised device. These devices are subject to more privilege and malware or virus threats. Jailbreak detection will require RootBeer on Android and DTTJailbreakDetection on iOS.
Secure network connections
- A Transport Secure Layer (TLS) should be used to exchange information and certificate pinning should be implemented to protect connections and attackers from accessing data via compromised certificates.
Utilise required permissions only
- Permissions can be enabled to access hardware and APIs through the app. By default, all plugins should be disabled if they contain unnecessary permissions.
User data security
- Where there is a need to store personally identifiable information or any other sensitive data, the Flutter_secure_storage package should be used.
Protection through background snapshots
- Flutter apps are vulnerable to exposing sensitive data through the feature that showcases a snapshot of the previous state of the app. The secure_application package can protect this content.
Implement local authentication
- Local_auth should be used as a plugin that supports authentication for Flutter apps. Biometric authentication should be implemented to protect apps storing payment information and local authentication should be used to provide protection in the event that the device is lost or stolen.
Developer identity security
- Encryption should be applied where there is a risk that the app may expose the identity of the developer. Sensitive files should be encrypted with GPG where they can be identified as key.jks and keystore.properties.
CI infrastructure security
- Code should be developed into a shared repository and vulnerabilities should be monitored in addition to updating Virtual Machine. Sensitive data should only be included in the secret settings.
Secure Coding for Flutter
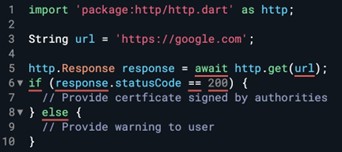
HTTPS
-
A secure layer must be inserted between the TCP communication layer and Transport Layer Security (TLS) to ensure the communication method for client- server applications is secure.
-
Upon connecting to the server, the client will receive the public key and all messages sent will be encrypted with only the server being able to decrypt messages through the private key. This prevents packet sniffers from reading the request details.
-
Communication should only be had with HTTPs endpoints and the server must either show the user a warning or issue a certificate that has been signed by authorities.
-
All URLs should commence with HTTPS. The http package can still be used.
Jailbroken and rooted devices
-
Jailbroken devices allow attackers to bypass security measures and import malware on devices.
-
Installation of flutter_jailbreak_detection will detect if the app is running on a device that is jailbroken or rooted.
-
It is compatible with Android devices and known as Root Beer and also on iOS devices known as DTT Jailbreak Detection
Encryption
-
Data should be encrypted in the Flutter app through converting the text into code to ensure it is only accessible through a key or password. This will protect it from unauthorised access
-
Algorithms such as AES or RSA can be used to encrypt data
-
Key management systems or secure storage locations
-
SSL/TLS protocols can be used to encrypt data in transit and secure communication channels between the client and server
-
Using certificate pinning can ensure the app only communicates with servers that have a trusted SSL/TLS certificate
Authenticating users and authorisation
-
Multi-factor authentication should be used to verify the identity of the users and improve security mechanisms
-
Rate limiting protocols could be used to prevent attackers from guessing a password a certain amount of times and time limitations can be set to prevent repeated attempts.
-
User credentials should be store via hashing and salting techniques to ensure passwords are not readable and vulnerable in data breach incidents
-
Access controls should be implemented to prevents certain users from accessing only data that is required for their role and minimises the risk of unauthorised access