Last updated by: KasparByrne, Last updated on: 23/09/2024
GATT Code
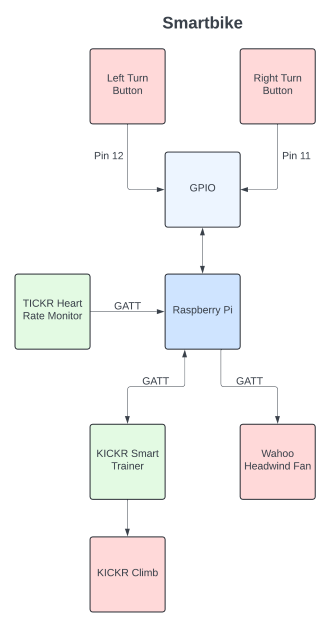
The Smartbike relies on BLE's GATT protocol for internal communication (between the Smartbike's components & Raspberry Pi). A gatt python library is used to drive this communication between the Raspberry Pi and the Smartbike's components.
Installing gatt library
To install run the following pip command:
pip install gatt
Import Library
The gatt library provides two classes which together manage and connect to BLE GATT enabled devices: DeviceManager & Device.
import gatt
DeviceManager
The DeviceManager class discovers and manages BLE devices.
# create a manager
manager = gatt.DeviceManager(adapter_name='hci0')
...
# create and connect managed device
device = gatt.Device('XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX', manager)
device.connect()
...
# run manager
manager.run()
...
# cleanly stop manager
manager.stop()
Initialisation
To initialise a DeviceManager pass it the BLE adapter address (most likely hc10):
manager = gatt.DeviceManager(adapter_name='hci0')
Managing Device
When creating a Device pass a DeviceManager to manage it:
device = gatt.Device('XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX', manager)
Run
To run call DeviceManager.run():
manager.run()
Terminate
To cleanly terminate use DeviceManager.stop():
manager.stop()
Device
The Device class is responsible for connecting to the device and discovering Services & Characteristics of the device.
Initialisation
device = gatt.Device(mac_address: str, manager: gatt.DeviceManager, managed: bool=True)
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
mac_address | str | the mac address of the target device |
manager | gatt.DeviceManager | A DeviceManager for managing the Device |
managed | bool [Default True] | In theory you could manage the device explicitly in which case you would set managed to False - but there is no reason to do this. |
Connecting to device
To connect using Device.connect():
device.connect()
The callback methods connect_succeeded and connect_failed can be overriden to log or handle any errors during connection.
Discovering Services & Characteristics
Upon successfully connecting to the device the services_resolved method is called. This method automatically discovers and appends all services of the device to the Device.services property and should be extended to discover any services or characteristics of interest like so:
class AnyDevice(gatt.Device):
...
def set_service_or_characteristic(self, service_or_characteristic):
# match using UUID
if service_or_characteristic.uuid == 'XXXXXXXX-XXXX-...':
self.service_or_characteristic_of_interest = service_or_characteristic
def service_resolve(self):
super().services_resolved()
for service in self.services:
self.set_service_or_characteristic(service)
for characteristic in service:
self.set_service_or_characteristic(characteristic)
...
# any other operations needed
Control Point Callbacks
After an operation is sent to a control point (read/writing a value, enabling notification, requesting control, etc) the control point will return a response. A set of callback methods should be overriden to perform any necessary operation's response:
| Callback Method | Parameters | Response Type |
|---|---|---|
characteristic_write_value_succeeded | characteristic | The characteristic write operation succeeded and the value has been updated |
characteristic_write_value_failed | characteristic, error | The characteristic write operation failed with the following error |
characteristic_enable_notification_succeeded | characteristic | Notification on the characteristic has been enabled |
characteristic_enable_notification_failed | characteristic, error | Notification has not been enabled on the requested characteristic with the following error |
characteristic_value_updated | characteristic, value | A notification enabled characteristic has updated with the following value |
These methods should be overriden to log, trigger methods for updated values, and handle errors.
Service
The Service class handles GATT services of devices. It has the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
uuid | The unique uuid of the service for identifying it |
characteristics | A list of the Service's Characteristics. |
Characteristic
The Characteristic class handles GATT characteristics of services/devices. It has a unique uuid for identification stored in its uuid property.
Reading Values
To read the value of a Characteristic use the Characteristic.read_value() method:
value = characteristic_of_interest.read_value()
Values are returned as an array of bytes. Depending on the expected use of the value it may be converted into a str or int, the bytes may also be a set of flags and values which require bit operations to extract the values from.
Enabling Notification
Better than explicitly reading a characteristic's value is being notified and given a value when the characteristic updates. Use the Characteristic.enable_notifications() method to enable notification. When the value is updated the Device callback method characteristic_value_updated is called.
Writing Values
Values written to a characteristic must be in a bytearray data type. To write a new value use the Characteristic.write_value():
# Convert the value to write into a bytes array
value_to_write = bytearray('Hello World!')
# write the value to the characteristic
characteristic_of_interest.write_value(value_to_write)
Updated gatt library
The version of the gatt library available through pip is outdated compared to the one available on the GitHub repo. As such a local updated version of the library has been created in the Drivers/lib/ folder under the gatt/ folder. To load this version use:
import lib.gatt.gatt_linux as gatt
Descriptor
This version contains the Descriptor class. Descriptors can hold useful meta data describing the expect values and use of a characteristic. In this version of the library, each Characteristic has a Descriptors array property:
description = characteristic_of_interest.descriptors
# convert to string
print(str(description))
Limited use of the Descriptor class and descriptors property has occurred - Wahoo devices appear to lack any meta data in their descriptors.
Further Information
- For more information on GATT protocol
- For the
gattlibrary's source code - For the
gattlibrary's documentation - For the updated
gattlibrary Drivers/lib/gatt/gatt_linux.py