Last updated by: SassafrasAU, Last updated on: 15/03/2024
Two Factor Authentication Bypass
Progress of 2FA in Redback
Author: Melvin Manoj
Introduction
The purpose of the document is to demonstrate the progress of two-factor authentication for Redback Operations from the previous trimesters. It consists of demonstrating vulnerability testing with evidence, on ways to bypass the two-factor authentications. Moreover, this document compiles all the evidence and research on vulnerabilities to give the next trimester students detailed implications of the projects and further advice on how to improve the two-factor authentication process. My role was to gather all the relevant documents and deliverables from the previous trimester and work on the progress to test the two-factor authentication find vulnerabilities and create a detailed document showcasing the vulnerabilities and ways to improve these in the next trimester. This handover document will consist of:
What is 2FA?
Redback operations have decided to implement 2FA two-factor authentication as an additional layer of security to ensure that only the users who are entitled to their accounts can access them. Traditional authentication relies on single-factor authentication, however, 2FA adds an extra step of security to the login process by requiring a second authentication method to verify the authentication. The common types of 2FA include:
-
SMS or Email Codes
-
Authentication apps
-
Hardware Tokens
-
Biometric Authentication
-
Push notifications
-
QR code
Each has its advantages and disadvantages. This document will discuss ways that 2FA can be bypassed and the vulnerabilities that need to be resolved for the next trimester.
Bypassing two-factor authentication
Man in the middle attack (MitM) using Evilginx2
Most phishing techniques are used by attackers who clone the login interface page and host it on their web server to gain access to the credentials. However, that can't always give the attackers access to the 2FA access code. Evilginx2 is a phishing tool that performs MitM attacks against websites that use two- factor authentication. It acts as a proxy connecting to 2FA-protected sites and acting as a passthrough from the victim -> server as shown in the illustration below:
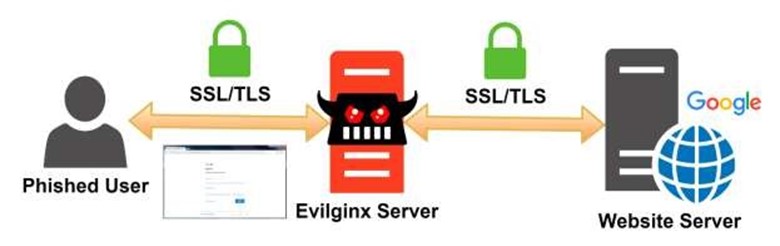
Evilginx2 acts as a proxy which means the user will see the contents of the site as exactly as they would when they visit the actual site. So the victim will see the login page for redback operations just as it would normally be. Attackers generate a phishing link and on successful sign-in from the victim the link will redirect the victim. The victim can receive this link via any available communication such as email, messenger, etc. The victim clicks on the link and will be presented with the Evilginx proxied sign-in page. After the victim enters the credentials to sign in, they will be redirected to the URL specified by the rc parameter. The rd cookie is saved for the domain in the victim's browser. From now on, if the cookie is present, the victim will be redirected to rc URl, when the phishing link is re-opened. Ultimately, attackers now have the victims' email and password, as well as session cookies that now can be imported into the attackers' browser to gain full access to the logged-in session, bypassing any two-factor authentication enabled on the victims' account.
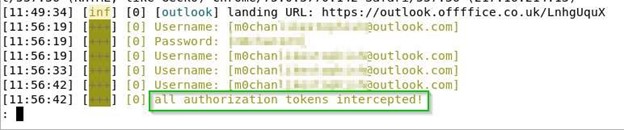
Evilginx2 can configure the files named ‘phishlets’ that are plain text rulesets in YAML format. These files direct which subdomains are needed to proxy a specific site, which cookies to capture, and which page to redirect the victim and capture their credentials. In the image above we can see Evilgenx2 has captured the user credentials and all the tokens are intercepted. This lets the attack hijack the user session using the authorized session tokens, using a cookie manager, and logging in without entering the username and password.
Monitor URL
The users need to be aware of the URL of the domain they are attempting to sign into. Redback Operations needs to train the staff and users to avoid damage. Users need to be trained on social engineering attacks and be careful what links they are clicking on.
Universal 2nd Factor
Universal 2 factors are hardware keys that have a clear security mechanism inbuilt where it will not issue a 2FA token if the domain does not match the legit domain
Pass the Cookie
User authentication information is stored by cookies in the web application, which lets the user stay signed in instead of logging in multiple times. Pass the cookie works in a way once the user has already logged on by verifying the 2FA a browser cookie is created and stored for the web session. The attack can then extract the right browser cookies, they can then access as another user in a separate web browser session on another system using the cookies to bypass the authentication via MFA.
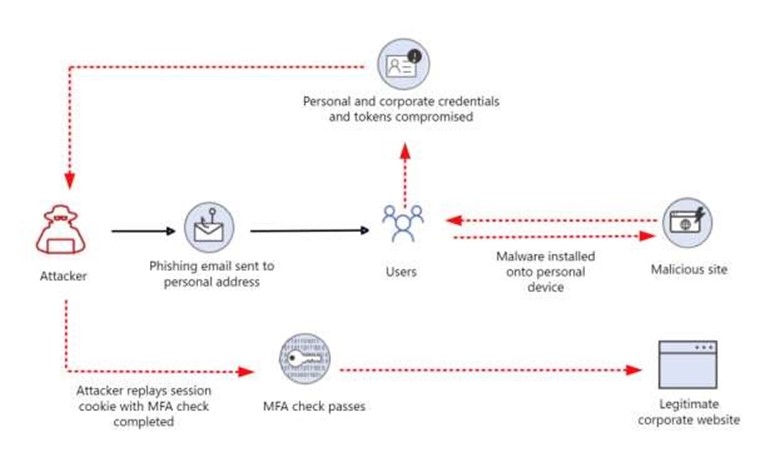
Name:Melvin Manoj ID:219187067 Universal 2 factors are hardware keys that have a clear security mechanism inbuilt where it will not issue a 2FA token if the domain does not match the legit domain. Pass the Cookie User authentication information is stored by cookies in the web application, which lets the user stay signed in instead of logging in multiple times. Pass the cookie works in a way once the user has already logged on by verifying the 2FA a browser cookie is created and stored for the web session. The attack can then extract the right browser cookies, they can then access as another user in a separate web browser session on another system using the cookies to bypass the authentication via MFA.
The attacker first extracts the cookies using this command:
mimikatz.exe privilege::debug log "dpapi::chrome
/in:%localappdata%googlechromeUSERDA~1defaultcookies /unprotect" exit
The attacker can then use the stolen cookies to inspect the stolen session by opening Chrome on another server and using the ‘inspect’ interface to insert a cookie. The attacker can navigate to pass the cookies to hijack the session and refresh the page. The attack then has access to the user account using the cookies that have already authenticated 2FA. The attack now can use the stolen web session to impersonate the victim user to access unauthorized data.
Using HTTPS
Encryption data transmission between user and browser using HTTPS can prevent attackers from intercepting sensitive information such as session cookies.
Secure Cookies
Secure Flag and HttpOnly flag ensure that the cookie is sent over HTTPS only and prevents JavaScript from accessing the cookie. Ultimately making it difficult for the attacker to steal the session cookie.
SMS Based Man in the Middle (MitM)
Attacks use an SMS MITM attack to gain unauthorized access to alter SMS messages between two parties. Attacks can use social engineering to trick phone companies into swapping SIMs then they can gain access to the SMS-based two-factor authentication for the victim as they are receiving all the SMS messages to the attack's phone without the victim realizing it. This attack takes control of the phone number and now has access to the 2FA code that is sent. This attack can bypass the OTP one-time password sent to the user by SMS as the attacker has access to the phone number. Moreover, once the attacker can reroute the messages they can also gain access to other accounts that phone number.
Using Additional Authentication
Using app-based 2FA or hardware tokens rather than relying on the SMS-based 2FA will create additional security for the user.
Attack on Hard and Soft Tokens
While software tokens like Google Authenticator or RSA’s SecureID Authenticate are generally considered secure, the nature of BYOD means organizations still have to worry about malware on the phones themselves. They generate a TOTP-based one-time password, the user has to download another app such as Microsoft Authenticator, Google Authenticator, etc, which produces a TOTP that the user has to enter to gain access after providing their credentials. These codes usually generate codes that are 6 digits long and refresh after every 30 seconds. This method is more secure than all the options discussed above, however, if the attacker gains access to the phone, they have access to the code and then can gain access to the account. Moreover, if the victim clicks on the phishing link that mimics the real website, the victim will provide the login and TOTP on the fake website which then the attacker can use on the real website to gain access to your account.
Defense
Avoid phishing links that are sent by email or SMS. The user needs to be aware of the risks of data breaches and needs to be informed about what the real website links should look like.
Moreover, we can use TOTP codes that are longer than 6 digits to help against brute force attacks, as the longer code will not give the attacks enough time to use brute force attack, as the password will reset in 30 seconds.
Conclusion
To conclude this report we have discussed the different ways the attackers can bypass the two-factor authentication to gain unauthorized access to the user account. The attackers can use Evilginx2, pass the cookie hijack, SIM-based man-in-the-middle attack, and brute force attack. The document covers each attack and how it can be a risk to the company and user data. I have discussed how the cyber security team and defend against these attacks. The document helps train the users and the cyber security team to understand the potential attacks. furthermore, it helps the cyber security team to come up with solutions and ways to prevent data breaches against these attacks.
References
https://m0chan.github.io/2019/07/26/Bypassing-2FA-For-Fun-With-Evilginx2.html
https://breakdev.org/evilginx-advanced-phishing-with-two-factor-authentication-bypass/
https://medium.com/@OWN_team/analysis-and-detection-of-mitm-phishing-attacks-bypassing-2fa- o365-use-case-cf0ffdae9cae
https://blog.netwrix.com/2022/11/29/bypassing-mfa-with-pass-the-cookie-attack/